RSPO2-based peptibodies conjugated with pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer or camptothecin analogs demonstrate potent anti-tumor activity by targeting the three receptors LGR4/5/6
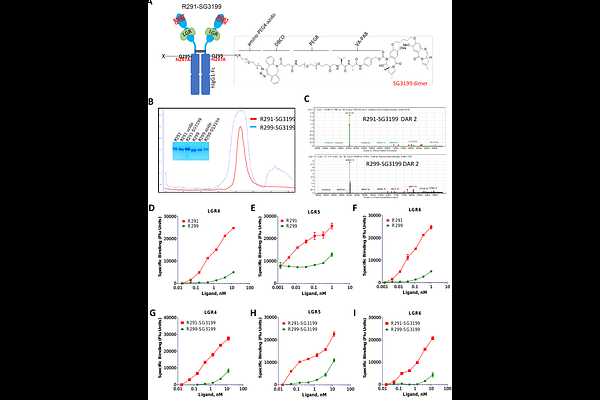
RSPO2-based peptibodies conjugated with pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer or camptothecin analogs demonstrate potent anti-tumor activity by targeting the three receptors LGR4/5/6
Toh, Y.; Tu, J.; Wu, L.; Aldana, A.; Wen, J. J.; Li, L.; Pan, S.; Liu, Q. J.
AbstractLGR4/5/6 (leucine-rich repeat containing, G protein-coupled receptors 4, 5, and 6) are three homologous receptors that are co-expressed or alternately expressed at high levels in tumor cells of colorectal cancer and high-risk neuroblastoma. Simultaneous targeting of all three receptors may provide increased efficacy or overcome drug resistance due to tumor heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. LGR4/5/6 all bind to R-spondins (RSPOs) with high affinity and potentiate Wnt/{beta}-catenin signaling in response. Previously, we showed that a peptibody based on a mutant RSPO4 furin domain that bound to LGR4/5/6 without potentiating Wnt/{beta}-catenin signaling was able to deliver cytotoxins into cancer cells that express any of the three receptors. We have now generated a mutant RSPO2 furin domain that retains high affinity binding to LGR4/5/6 without signaling activity. Peptibodies based on this RSPO2 furin mutant were conjugated with either pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer or camptothecin derivative, and the resulting peptibodydrug conjugates (PDCs) showed potent and specific cytotoxic activity in neuroblastoma and colorectal cancer cell lines expressing any of LGR4/5/6 in vitro and robust anti-tumor activity in vivo. The results support the potential of RSPO2-based PDCs for the treatment of colorectal cancer, high-risk neuroblastoma, and other cancers that express LGR4/5/6.