SHLD2 loss is a synthetic vulnerability to Polθ inhibition combined with radiotherapy
SHLD2 loss is a synthetic vulnerability to Polθ inhibition combined with radiotherapy
Rodriguez-Berriguete, G.; Thambiayah, P.; Cicconi, A.; Machado, N.; Gotorbe, C.; Nderitu, D.; Cheng, W.-C.; Boursier, M. L.; Cerutti, A.; Grinkevich, V.; Hill, B. R.; Koler, K.; Langdon, S. A.; Majithiya, J. B.; Menon, S.; Moore, S.; Neves, J.; Palmer-Deverill, N. M.; Rajendra, E.; Roy-Luzarraga, M.; Thapa, A.; Heald, R. A.; Smith, G. C. M.; Robinson, H. M. R.; Ranzani, M.; Higgins, G. S.
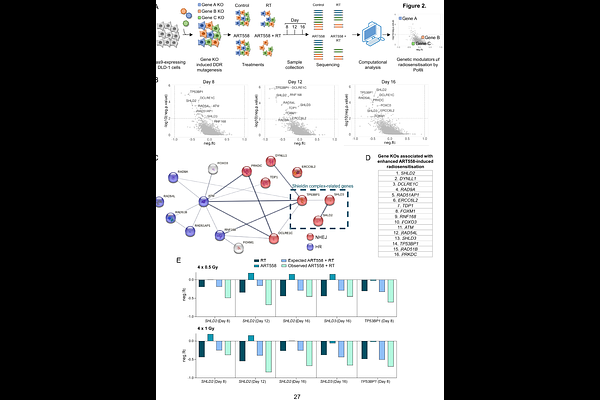
AbstractDNA polymerase theta (Pol{theta}) plays a crucial role in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ). We previously demonstrated that Pol{theta} inhibition (Pol{theta}i) is an effective and well-tolerated approach to sensitise tumours to radiotherapy (RT). Here, we profiled 54 cancer cell lines and found that Pol{theta}i induces significant radiosensitisation in most models, though with marked variability not explained by indicators of Pol{theta} activity. To pinpoint molecular determinants of radiosensitisation by Pol{theta}i, we performed a CRISPR knockout screen which revealed loss of the TP53BP1/Shieldin pathway component SHLD2 (FAM35A) as a vulnerability to Pol{theta}i combined with RT. We demonstrated that SHLD2 loss not only increases sensitivity to RT alone, but also enhances the radiosensitising effect of Pol{theta}i, both in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, we found that SHLD2 is deleted in a subset of human prostate cancers, often co-occurring with PTEN loss, an adverse prognostic factor. Furthermore, we show that SHLD2-deficient cancer cells are more reliant on Pol{theta} to prevent DSB accumulation and chromosomal instability. In summary, we discovered SHLD2 loss as a novel collateral vulnerability that can be exploited through combined treatment with Pol{theta}i and RT.