HPV16 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies show evidence for common developmental pathways and public epitopes
HPV16 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies show evidence for common developmental pathways and public epitopes
Carter, J. J.; Hurlburt, N. K.; Scherer, E. M.; Singh, S.; Rodarte, J. V.; Smith, R. A.; Lewis, P.; Kinzelman, R. J.; Kieltyka, J.; Caban, M. E.; Wipf, G. C.; Pancera, M.; Galloway, D. A.
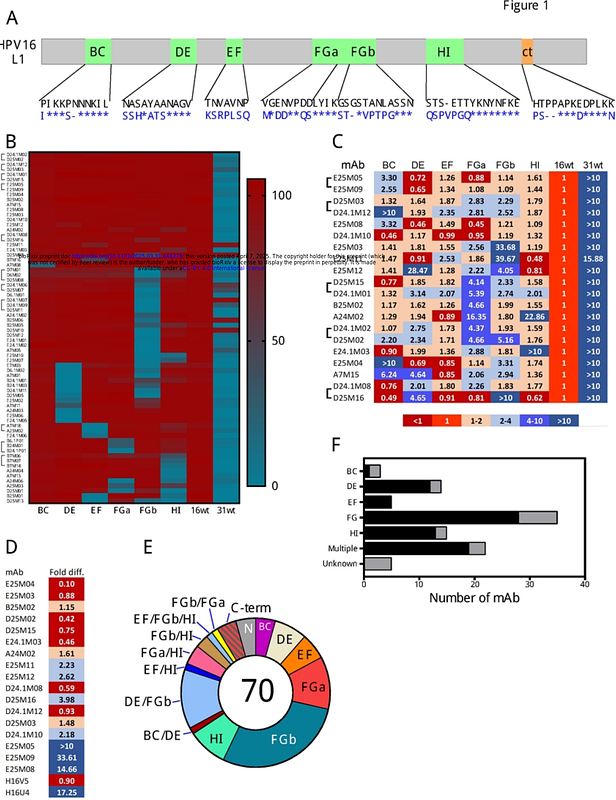
AbstractAntibodies to human papillomavirus (HPV) primarily recognize surface exposed residues on five loops of the major capsid protein (L1) that vary significantly among HPV types. We determined which loops were required for neutralization for 70 HPV16 specific human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) cloned from participants who received an HPV vaccine, and we describe molecular features of those antibodies. Chimeric HPV16 pseudovirus (cpsV), each having one surface loop bearing multiple amino acid substitutions, were used to determine neutralization specificity. The HPV16-FG-loop was the loop most frequently required for neutralization (44 of 70, 62.9%), however, all other surface loops were used for neutralization by multiple mAbs: HI (13, 18.6%), DE (15, 21.4%), EF (six, 8.6%), BC (four, 5.7%). Antibodies that required multiple loops were common (17, 24.3%). Three mAbs (4.3%) required sequences on the c-terminus of L1 and for another three mAbs the neutralization specificity could not be determined. Two types of mAbs appeared to be overrepresented: ten mAbs used VH 2-70 IGHV paired with VL l1-40, having characteristic mutations in complementarity determining region two (CDRL2). Cryogenic electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) revealed that two of these antibodies bound five Fabs per pentamer interacting with all five L1-surface loops. The other type of mAbs that appeared to be overrepresented were ten mAbs using VH 4-34, seven of which also used DH3-16*02 with conserved CDRH3 sequences. Cryo-EM for one of these mAbs, that required the FG-loop for neutralization, was shown to bind one Fab per pentamer at the apex, interacting with the DE- and FG-loops, with sequences of the Fab CDRH3 inserted between the DE- and FG-loops from two protomers. These two types of mAbs were found repeatedly in the four participants suggesting that these antibodies shared developmental pathways and bound to similar immunodominant epitopes on the virus.