Identification of Raptor and GLI1 as USP37 substrates highlight its context-specific function in medulloblastoma cells.
Identification of Raptor and GLI1 as USP37 substrates highlight its context-specific function in medulloblastoma cells.
Singh, A.; Cheng, D.; Haltom, A.; Yang, Y.; Dobson, T.; Hatcher, R.; Rajaram, V.; Gopalakrishnan, V.
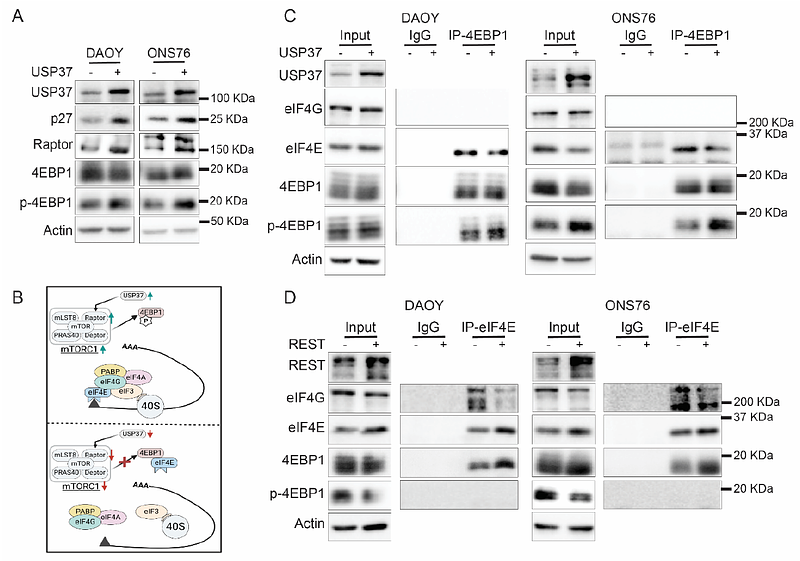
AbstractUSP37 gene encodes a deubiquitylase (DUB), which catalyzes the proteolytic removal of ubiquitin moieties from proteins to modulate their stability, cellular localization or activity. Its expression is downregulated in a subgroup of medulloblastomas driven by constitutive activation of sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling. Patients with SHH-driven medulloblastomas with elevated expression of the RE1 silencing transcription factor (REST) and reduced expression of USP37 have poor outcomes. In previous studies, we showed sustained proliferation of SHH-medulloblastoma cells due to blockade of terminal cell cycle exit and neuronal differentiation stemming from a failure in USP37-dependent stabilization of its target, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKI)-p27. This finding suggested a tumor suppressive function for USP37. Interestingly, the current study also uncovered Raptor, a component of the mTORC1 complex, as a novel target of USP37. Under conditions of low-USP37 expression, reduced Raptor stability and mTORC1 activity caused a decline in phosphorylation of 4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1) and increased its interaction with eukaryotic elongation factor 4E (eIF4E), which is known to inhibit CAP-dependent translation initiation. Surprisingly, a subset of patients with SHH-driven medulloblastomas with elevated expression of USP37 and the Glioma associated Oncogene 1 (GLI1), also exhibited poor outcomes. Using genetic and biochemical analyses, we showed that USP37-mediated stabilization of GLI1, a terminal effector of SHH signaling, increases pathway activity and upregulates expression of its target oncogene products, NMYC and CCND1, to drive cell proliferation. These data indicate that USP37 elevation in SHH-driven medulloblastomas has the potential to promote non-canonical activation of SHH signaling. Overall, our findings suggest that USP37 may have context-specific oncogenic and tumor suppressive roles in medulloblastoma cells.