B cells maintain the homeostasis of splenic marginal zone antigen-presenting cells to promote the anti-viral CD8+ T cell response
B cells maintain the homeostasis of splenic marginal zone antigen-presenting cells to promote the anti-viral CD8+ T cell response
Xin, X.; Demircik, F.; Antipova, M.; Stylianakis, E.; Klein, M.; Bejarano, D. A.; Elwy, A.; Ebering, A.; Blanfeld, M.; Carter, K.; Johann, L.; Uhlfelder, D.; Blickberndt, E.; Probst, H. C.; Hoevelmeyer, N.; Bopp, T.; Arens, R.; den Haan, J. M.; Gommerman, J.; von Stebut, E.; Clausen, B.; Schlitzer, A.; Lang, K. S.; Becker, R. A.; Lemmermann, N.; Waisman, A.
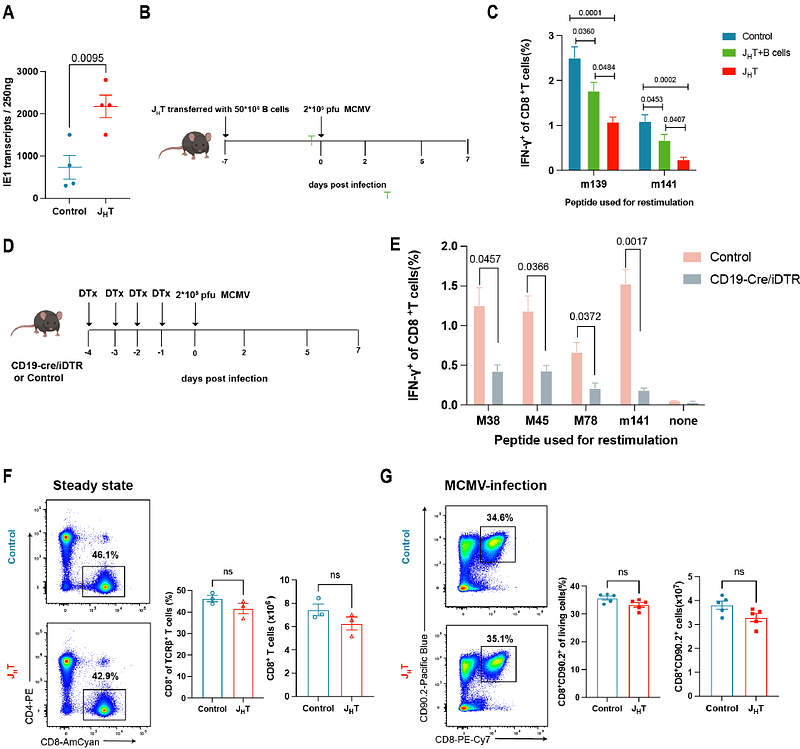
AbstractNatural killer and CD8+ T cells are critical in the elimination of blood-borne viruses such as cytomegalovirus (CMV); however, the role of B cells in this process is less clear. Here, using the murine CMV (MCMV) infection model, we demonstrated that the B cell-deficient mice mounted a weaker primary virus-specific CD8+ T cell response than their wild-type counterparts, which was associated with increased viral transcription. Notably, we found that the contribution of B cells to the CD8+ T-cell-mediated anti-viral response was not associated with their ability to generate antibodies but with their ability to sustain Langerin+ type 1 conventional dendritic cells (cDC1s), a dendritic cells (DC) subset known for being involved in viral and bacterial clearance in the marginal zone of the spleen. Furthermore, we found that the presence of Langerin+ cDC1s is dependent on B cells expressing lymphotoxin beta to maintain CD169+ marginal metallophilic macrophages (MMMs). We further discovered, using ligand-receptor interaction analyses, that the communication between MMMs and Langerin+ cDC1s was mediated via VCAM1 - ITGA4/ITGB1 interaction. Thus, our data reveals that B cell regulate the development of MMMs in the spleen via lymphotoxin beta; expression and consequently sustain Langerin+ cDC1s homeostasis for effective initiation of an anti-viral CD8+ T cell response. Overall, our study offers a new perspective on how B cells maintain the homeostasis of antigen-presenting cells in the splenic marginal zone and thus indirectly affect the virus-specific CD8+ T cell response, which could potentially be extended to other infectious and autoimmune diseases as well as tumors.