Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 protects against adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance but promotes liver inflammation and hepatic fibrosis in mice
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 protects against adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance but promotes liver inflammation and hepatic fibrosis in mice
Eswaran, S.; Gebert, L.; Schraven, S.; Treichel, N. S.; Ritz, T.; Hamm, S.; Seeger, A.; Kiessling, F.; Clavel, T.; Wagner, N.; Schippers, A.
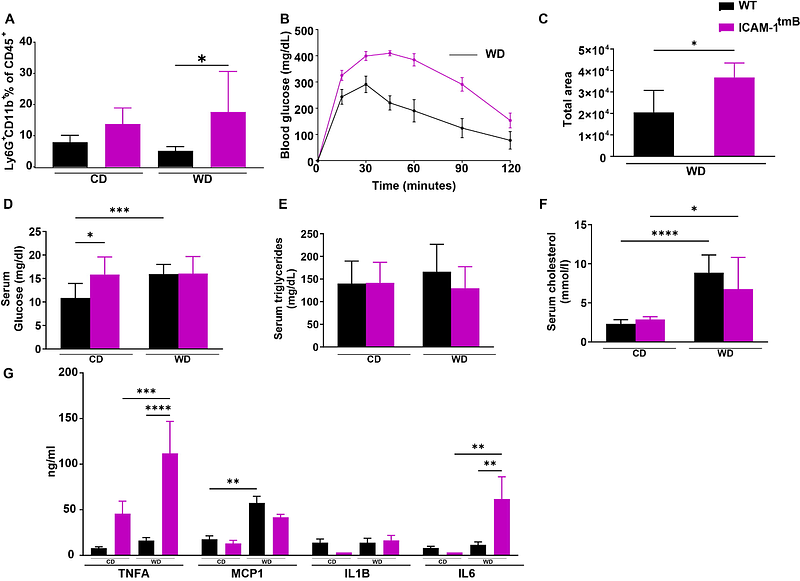
AbstractMetabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) presents a growing global health problem with a range of manifestations, including steatosis, steatohepatitis, and cirrhosis. It is strongly associated with obesity, disease progression being promoted not only by hepatic leukocyte accumulation but also by inflammatory signals from adipose tissue and an altered gut microbiome. To determine the contribution of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) to MASLD pathogenesis, mice with an ICAM-1 mutation (Icam1tmBay) were compared to wild type (WT) mice in a Western-style diet (WD) model. WD-induced MASLD was accompanied by increased ICAM-1 expression in liver, epididymal white adipose tissue (EWAT), and intestine in WT mice. WD-fed Icam1tmBay mice exhibited increased circulating neutrophils, higher frequencies of inflammatory leukocytes in EWAT, and a worsened glucose tolerance when compared to WT mice. In contrast, the mutation resulted in reduced WD-induced liver damage and less accumulation of intrahepatic leukocytes. WD-feeding caused substantial changes in fecal microbiota with decreased microbial diversity that differed between the mouse strains. In conclusion, ICAM-1 positively regulates adipose tissue homeostasis and protects from insulin resistance but promotes liver damage in diet-induced obesity. This points to various organ-specific roles for ICAM-1 and the potential of liver-specific targeting of ICAM-1 for treatment of MASLD.