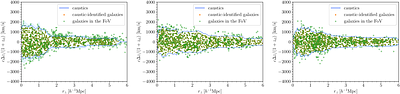
By: Renzhi Su, Stephen J. Curran, Francoise Combes, Neeraj Gupta, Sebastien Muller, Di Li, Minfeng Gu
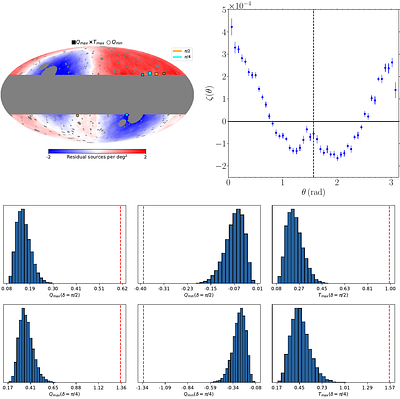
By: Akhil Antony, Stephen Appleby, William L Matthewson, Arman Shafieloo
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters
By: Hironao Miyatake
By: Yogesh, Abolhassan Mohammadi, Qiang Wu, Tao Zhu
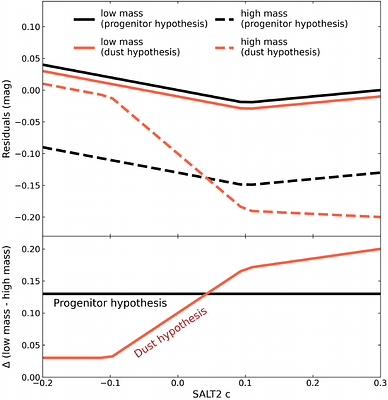
By: Yukei S. Murakami, Daniel Scolnic
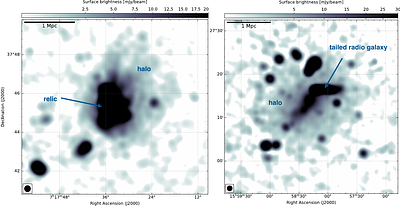
By: K. Rajpurohit, A. Botteon, E. O'Sullivan, W. Forman, M. Balboni, L. Bruno, R. J. van Weeren, M. Hoeft, G. Brunetti, C. Jones, A. S. Rajpurohit, S. P. Sikhosana
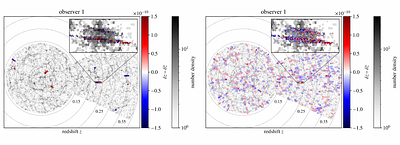
By: Alexander Oestreicher, Chris Clarkson, Julian Adamek, Sofie Marie Koksbang
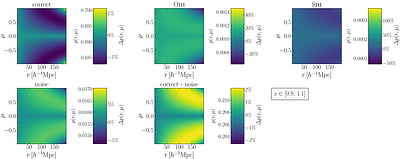
By: Euclid Collaboration, I. Risso, A. Veropalumbo, E. Branchini, E. Maragliano, S. de la Torre, E. Sarpa, P. Monaco, B. R. Granett, S. Lee, G. E. Addison, S. Bruton, C. Carbone, G. Lavaux, K. Markovic, K. McCarthy, G. Parimbelli, F. Passalacqua, W. J. Percival, C. Scarlata, E. Sefusatti, Y. Wang, M. Bonici, F. Oppizzi, N. Aghanim, B. Altieri, A. Amara, S. Andreon, N. Auricchio, C. Baccigalupi, M. Baldi, A. Balestra, S. Bardelli, P. Battaglia, A. Biviano, A. Bonchi, D. Bonino, M. Brescia, J. Brinchmann, S. Camera, G. Cañas-Herrera, V. Capobianco, V. F. Cardone, J. Carretero, S. Casas, M. Castellano, G. Castignani, S. Cavuoti, K. C. Chambers, A. Cimatti, C. Colodro-Conde, G. Congedo, C. J. Conselice, L. Conversi, Y. Copin, F. Courbin, H. M. Courtois, M. Crocce, A. Da Silva, H. Degaudenzi, G. De Lucia, A. M. Di Giorgio, H. Dole, M. Douspis, F. Dubath, C. A. J. Duncan, X. Dupac, S. Dusini, S. Escoffier, M. Farina, R. Farinelli, F. Faustini, S. Ferriol, F. Finelli, S. Fotopoulou, N. Fourmanoit, M. Frailis, E. Franceschi, M. Fumana, S. Galeotta, K. George, W. Gillard, B. Gillis, C. Giocoli, J. Gracia-Carpio, A. Grazian, F. Grupp, L. Guzzo, S. V. H. Haugan, W. Holmes, F. Hormuth, A. Hornstrup, P. Hudelot, K. Jahnke, M. Jhabvala, B. Joachimi, E. Keihänen, S. Kermiche, A. Kiessling, M. Kilbinger, B. Kubik, M. Kümmel, M. Kunz, H. Kurki-Suonio, A. M. C. Le Brun, P. Liebing, S. Ligori, P. B. Lilje, V. Lindholm, I. Lloro, G. Mainetti, D. Maino, E. Maiorano, O. Mansutti, S. Marcin, O. Marggraf, M. Martinelli, N. Martinet, F. Marulli, R. Massey, S. Maurogordato, E. Medinaceli, S. Mei, M. Melchior, Y. Mellier, M. Meneghetti, E. Merlin, G. Meylan, A. Mora, M. Moresco, L. Moscardini, R. Nakajima, C. Neissner, S. -M. Niemi, J. W. Nightingale, C. Padilla, S. Paltani, F. Pasian, K. Pedersen, V. Pettorino, S. Pires, G. Polenta, M. Poncet, L. A. Popa, L. Pozzetti, F. Raison, R. Rebolo, A. Renzi, J. Rhodes, G. Riccio, E. Romelli, M. Roncarelli, E. Rossetti, R. Saglia, Z. Sakr, D. Sapone, B. Sartoris, J. A. Schewtschenko, P. Schneider, T. Schrabback, M. Scodeggio, A. Secroun, G. Seidel, M. Seiffert, S. Serrano, P. Simon, C. Sirignano, G. Sirri, L. Stanco, J. Steinwagner, C. Surace, P. Tallada-Crespí, D. Tavagnacco, A. N. Taylor, I. Tereno, N. Tessore, S. Toft, R. Toledo-Moreo, F. Torradeflot, I. Tutusaus, L. Valenziano, J. Valiviita, T. Vassallo, G. Verdoes Kleijn, D. Vibert, J. Weller, G. Zamorani, F. M. Zerbi, E. Zucca, V. Allevato, M. Ballardini, M. Bolzonella, E. Bozzo, C. Burigana, R. Cabanac, A. Cappi, D. Di Ferdinando, J. A. Escartin Vigo, L. Gabarra, W. G. Hartley, J. Martín-Fleitas, S. Matthew, N. Mauri, R. B. Metcalf, A. Pezzotta, M. Pöntinen, C. Porciani, V. Scottez, M. Sereno, M. Tenti, M. Viel, M. Wiesmann, Y. Akrami, S. Alvi, I. T. Andika, M. Archidiacono, F. Atrio-Barandela, S. Avila, A. Balaguera-Antolinez, C. Benoist, D. Bertacca, M. Bethermin, L. Blot, H. Böhringer, S. Borgani, M. L. Brown, A. Calabro, B. Camacho Quevedo, F. Caro, C. S. Carvalho, T. Castro, F. Cogato, A. R. Cooray, O. Cucciati, S. Davini, F. De Paolis, G. Desprez, A. Díaz-Sánchez, J. J. Diaz, S. Di Domizio, J. M. Diego, P. Dimauro, A. Enia, Y. Fang, A. G. Ferrari, A. Finoguenov, A. Fontana, A. Franco, K. Ganga, J. García-Bellido, T. Gasparetto, V. Gautard, E. Gaztanaga, F. Giacomini, F. Gianotti, G. Gozaliasl, M. Guidi, C. M. Gutierrez, A. Hall, S. Hemmati, C. Hernández-Monteagudo, H. Hildebrandt, J. Hjorth, S. Joudaki, J. J. E. Kajava, Y. Kang, V. Kansal, D. Karagiannis, K. Kiiveri, C. C. Kirkpatrick, S. Kruk, V. Le Brun, J. Le Graet, L. Legrand, M. Lembo, F. Lepori, G. Leroy, G. F. Lesci, L. Leuzzi, T. I. Liaudat, A. Loureiro, J. Macias-Perez, M. Magliocchetti, F. Mannucci, R. Maoli, C. J. A. P. Martins, L. Maurin, M. Miluzio, C. Moretti, G. Morgante, S. Nadathur, K. Naidoo, A. Navarro-Alsina, K. Paterson, L. Patrizii, A. Pisani, D. Potter, S. Quai, M. Radovich, P. -F. Rocci, S. Sacquegna, M. Sahlén, D. B. Sanders, A. Schneider, D. Sciotti, E. Sellentin, L. C. Smith, J. G. Sorce, K. Tanidis, C. Tao, G. Testera, R. Teyssier, S. Tosi, A. Troja, M. Tucci, C. Valieri, A. Venhola, D. Vergani, G. Verza, N. A. Walton
Cluster Lensing Mass Inversion (CLUMI+): Combining Dynamics and Weak Lensing around Galaxy Clusters
By: Keiichi Umetsu, Michele Pizzardo, Antonaldo Diaferio, Margaret J. Geller
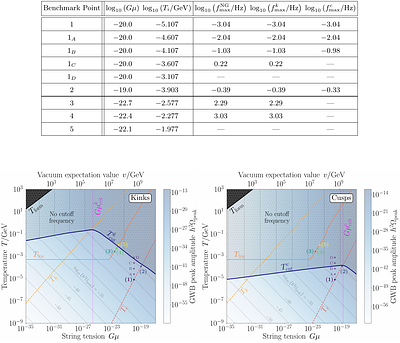
By: Kai Schmitz, Tobias Schröder