LOSS OF ROR2 TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTOR IS ASSOCIATED WITH ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION IN PAH VIA INAPPROPRIATE INTEGRIN BETA 1 ACTIVATION
LOSS OF ROR2 TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTOR IS ASSOCIATED WITH ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION IN PAH VIA INAPPROPRIATE INTEGRIN BETA 1 ACTIVATION
Mitra, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Zhong, B.; Heo, L.; Agarwal, S.; Pacheco, A.; Auer, N.; Dunn, A.; Chelladurai, P.; Jain, A.; Matos, J.; Bankar, A.; Guardado, E.; YI, D.; Zhao, H.; Wai Dede Man, K.; Nair, R. V.; Guenat, O. T.; Dai, Z.; de Jesus Perez, V. A.
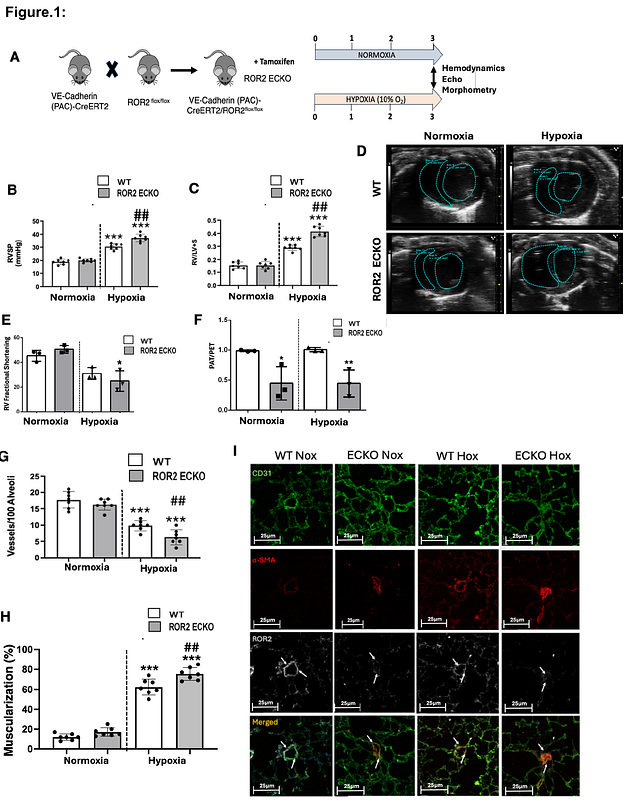
AbstractRationale: Endothelial dysfunction is a key feature of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). We previously identified Wnt7a, a ligand of the Wnt planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway, as essential for pulmonary angiogenesis, with its loss linked to PAH. Given the importance of Wnt/PCP to lung endothelial function and angiogenesis, our goal is to elucidate how Wnt/PCP regulates angiogenic responses in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs). ROR2, a tyrosine kinase receptor specific to Wnt/PCP, is crucial for cardiovascular development, but its role in PAH is unclear. We hypothesized that ROR2 supports endothelial homeostasis, and its loss would impair angiogenesis, contributing to PAH. Methods: Endothelial-specific ROR2 knockout (ROR2 ECKO) and wild-type (WT) mice were studied under normoxia and chronic hypoxia using echocardiography, hemodynamics, and lung morphometry. PMVECs from healthy and PAH lungs were transfected with ROR2 siRNA/constructs for functional and molecular studies. Focal adhesion (FA) activation and force generation were assessed via FRET-based methods. Bulk and single-cell transcriptomic analyses were performed on siROR2 PMVECs and ROR2 ECKO lungs. Results: ROR2 ECKO mice exhibited worsened pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular remodeling, microvascular loss, and muscularization in hypoxia. Single-cell RNA sequencing of lung endothelial cells showed dysregulation of pathways involved in barrier formation and angiogenesis. Evans blue dye extravasation confirmed reduced endothelial barrier integrity in ROR2 ECKO mice. ROR2-deficient PAH PMVECs displayed increased adhesion, permeability, and FA numbers, with reduced VE-cadherin at cell junctions. Confocal imaging revealed ROR2 localization in FAs, interacting with integrin ?1 (ITGB1). FRET analysis showed that ITGB1 remained in an active, adhesion-promoting state in ROR2-deficient cells. Restoring ROR2 in PAH PMVECs normalized adhesion, barrier function, and FA abundance. Transcriptomic analysis identified Rab12 as a key mediator of ROR2-ITGB1 crosstalk, with Rab12 knockdown mimicking ROR2 deficiency in PMVECs. Conclusions: ROR2 regulates pulmonary angiogenesis by maintaining endothelial barrier integrity and facilitating integrin recycling. Restoring ROR2 signaling could be a potential therapeutic approach for PAH.