A meta-analysis of periodic and aperiodic M/EEG components in Parkinson's disease
A meta-analysis of periodic and aperiodic M/EEG components in Parkinson's disease
Norouzi, H.; Ietswaart, M.; Adair, J.; Learmonth, G.
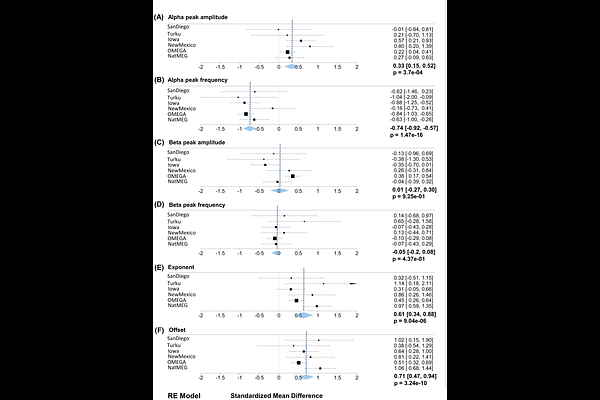
AbstractParkinson\'s disease is characterised by a range of motor and non-motor changes that can negatively impact quality of life. Many studies have identified potential clinical electrophysiological biomarkers of Parkinson\'s disease with an aim of developing new methods of identifying at-risk patients, and to form the basis of therapeutic interventions. However, these studies do not present consistent results, and a formal meta-analysis is warranted to identify reliable M/EEG characteristics across datasets. In this meta-(re-)analysis of open-access M/EEG datasets (n = 6; 4 EEG and 2 MEG), we compared periodic and aperiodic characteristics of resting-state recordings in 368 patients with Parkinson\'s disease and 570 age-matched healthy controls. Specifically, we compared the power and peak frequency of the aperiodic-adjusted alpha and beta oscillations, and the aperiodic exponent and offset across the two groups. Using spectral parametrisation, individuals with Parkinson\'s disease had higher alpha-band power and a slower alpha peak frequency compared to controls, however no group differences in beta-band power and peak frequency were identified in this resting state data. Parkinson\'s patients were furthermore found to have consistently higher aperiodic offset and exponent, possibly indicative of increased cortical inhibition. In conclusion, this large cohort meta-analysis points to a broadly consistent pattern of both periodic and aperiodic changes in Parkinson\'s patients in M/EEG signal that may be used to develop diagnostics and targeted interventions in the future.