NCR13 peptide protects soybean against Cercospora sojina by multiple modes of action and additive interaction with chemical fungicides
NCR13 peptide protects soybean against Cercospora sojina by multiple modes of action and additive interaction with chemical fungicides
Pokhrel, A.; Nath, V. S.; Godwin, J.; Kalunke, R.; TETORYA, M.; Czymmek, K. J.; Shah, D. M.
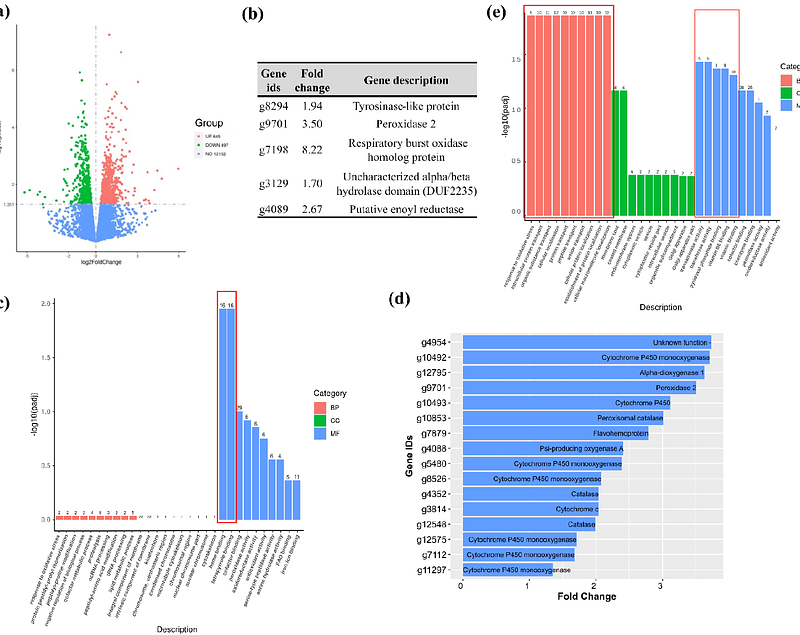
AbstractFrogeye Leaf Spot (FLS) disease, caused by a fungal pathogen Cercospora sojina, is a serious threat to soybean production globally. The control of FLS is facing a major challenge due to the rapid emergence of pathogen resistance to Quinone outside Inhibitor (QoI) fungicides. Effective long-term management of FLS in soybean calls for the discovery of antifungal compounds with new modes of action (MoA), durability and safety. Here, we showed that chickpea nodule-specific cysteine-rich peptide, NCR13_Peptide Folding Variant1 (NCR13_PFV1), exhibited antifungal activity against QoI-sensitive and -resistant field isolates of C. sojina at nanomolar concentrations representing the first antifungal NCR peptide reported effective against C. sojina. Spray-application of this peptide showed no phytotoxicity and effectively protected soybean against FLS. When combined with the QoI fungicide azoxystrobin, NCR13_PFV1 provided additive control of FLS. NCR13_PFV1 induced plasma membrane disruption and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in C. sojina. NCR13_PFV1 was rapidly internalized into fungal cells where it accumulated in the cytoplasm, localized inside nucleus, bound to fungal ribosomal RNA and inhibited protein translation in vivo. RNA-seq studies revealed the upregulation of several genes encoding heme binding proteins in peptide-challenged C. sojina. Notably, iron supplementation in the growth medium reduced the peptide-induced ROS and antifungal activity, revealing the importance of iron homeostasis in protection or recovery of C. sojina from oxidative stress. Overall, NCR13_PFV1 with multiple MoA holds potential as a bio-fungicide for FLS control complementing conventional QoI fungicides and overcoming fungicide resistance in C. sojina.