Overcoming effects of heterogeneous binding on BLI analysis
Overcoming effects of heterogeneous binding on BLI analysis
Sherer, N.; Cho, J.-H.
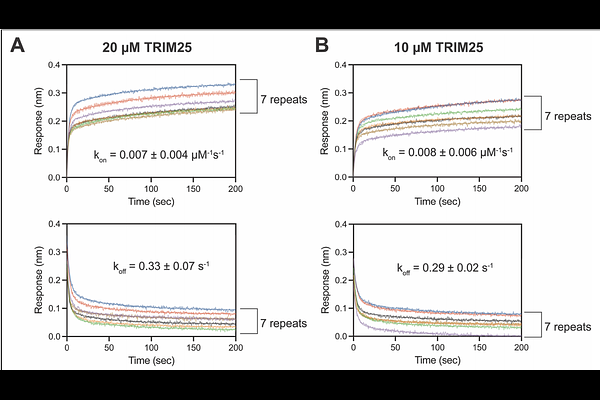
AbstractBinding characteristics, such as kon, koff, and KD, are critical for mechanistic study of biomolecular interactions and drug design. Biolayer interferometry (BLI) has become popular due to its simplicity and sensitivity. Despite its widespread use, BLI data analysis is susceptible to various non-ideal features in sensorgrams. One commonly observed issue is a persistent signal drift after the binding process reaches an expected steady state. The basis of this phenomenon, often referred to as heterogeneous binding, remains poorly understood. In this study, we find that analyte aggregation on the biosensor, particularly induced by ligand-analyte complexes, can contribute to heterogeneous binding. We also find that heterogeneous binding affects not only the association phase but also the dissociation process, leading to erroneous binding characteristics. We propose an approach to mitigate the adverse impacts of heterogeneous binding on the BLI analysis. Since accurate binding characterization is fundamental for many biophysical analyses, addressing this issue is crucial.