Design of Tau Aggregation Inhibitors Using Iterative Machine Learning and a Polymorph-Specific Brain-Seeded Fibril Amplification Assay
Design of Tau Aggregation Inhibitors Using Iterative Machine Learning and a Polymorph-Specific Brain-Seeded Fibril Amplification Assay
Santambrogio, A.; Horne, R. I.; Metrick, M. A.; Brotzakis, Z. F.; Rinauro, D.; Vourkou, E.; Skoulakis, E. M.; Linse, S.; Caughey, B.; Vendruscolo, M.
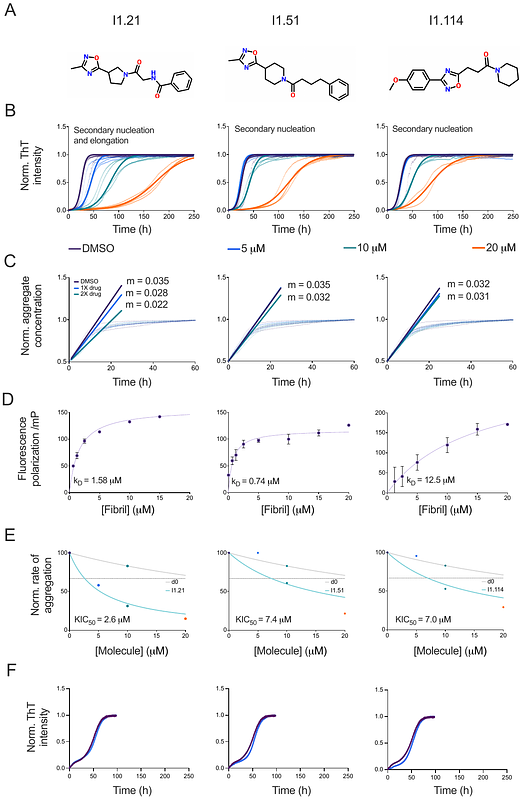
AbstractThe aggregation of tau into amyloid fibrils is associated with Alzheimer\'s disease (AD) and related tauopathies. Since different tauopathies are characterised by the formation of distinct tau fibril morphologies, it is important to combine the search of tau aggregation inhibitors with the development of in vitro tau aggregation assays that recapitulate aggregation as it may occur in the brain. Here we address this problem by reporting an in vitro tau aggregation assay in which AD brain homogenates are used to seed the generation of first-generation tau fibrils in a polymorph-specific manner under quiescent conditions. These fibrils are then used to create amyloid seed libraries from which second-generation kinetic assays can be readily performed. Using this strategy, we illustrate an iterative machine learning method for the identification of small molecules for the polymorph-specific inhibition of the in vitro formation of tau fibrils. We further show that the small molecules selected by this procedure are potent inhibitors in a Drosophila tauopathy model.