Identification of functional neural networks of human brains with fMRI
Identification of functional neural networks of human brains with fMRI
Huang, J.
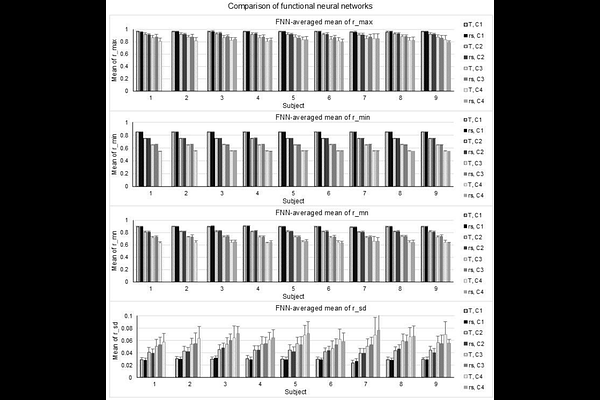
AbstractThe highly evolved human brain comprises numerous functional systems, ranging from essential sensory, motor, attention and memory networks to higher-order cognitive functions like reasoning and language. Although these neural systems and cognitive functions are separately distributed across the entire brain, they are functionally integrated together to perform a task. Decision-making and executive functioning may also be involved in performing the task. While studying task-evoked brain networks is important, investigating whole-brain activity could be crucial for understanding the neural underpinnings of individual behavioral and clinical traits. Even when the brain is not actively engaged in a task, the intrinsic neural activity, i.e., the resting-state (rs) activity, maintains the operations of the brain that involve the acquisition and maintenance of information for interpreting, responding to, and predicting environmental demands. This intrinsic activity is also functionally organized into networks like the brain default mode network. Investigating its whole-brain activity could also be crucial for understanding the neural underpinnings of the operations of the brain at rest. We report a novel data-driven method to objectively and automatically identify functional neural networks (FNNs) across the entire brain for both brain states measured with rs- and task-fMRI, respectively. The identified FNNs characterize the whole-brain activity holistically for each brain state and each individual subject.