On Neutron Star Natal Kicks in High-Mass X-Ray Binaries: Insights from Population Synthesis
On Neutron Star Natal Kicks in High-Mass X-Ray Binaries: Insights from Population Synthesis
Xiangyu Ivy Wang, Xiang-Dong Li
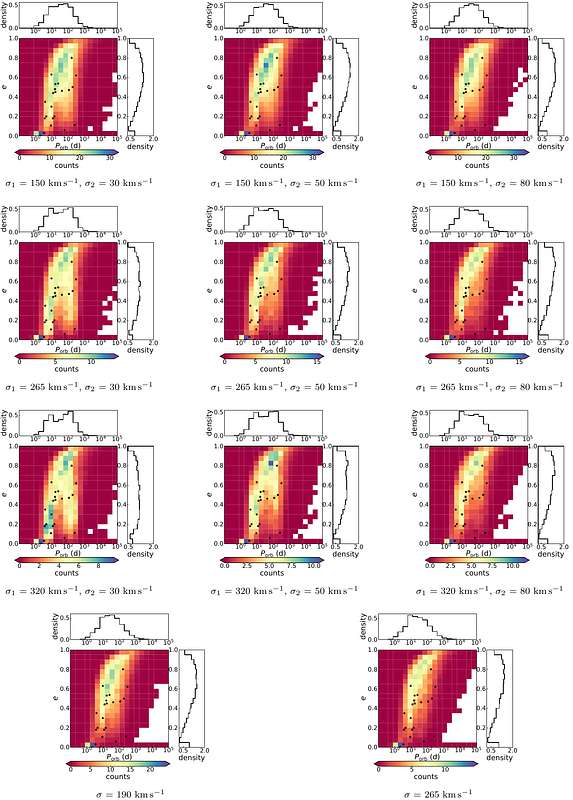
AbstractThe motion of neutron stars (NSs) in the Galaxy is largely dependent on natal kicks received by the NSs during supernova explosions. Thus, the measured peculiar velocities of NS high-mass X-ray binaries (HMXBs) provide valuable clues to natal kicks, which also play an important role in the evolution of HMXBs. In this work, we collect proper motions, radial velocities and parallaxes for 36 NS HMXBs to derive their peculiar velocities at the birth of the NSs. We then use binary population synthesis to simulate the velocities of NS HMXBs with various choices of the kick velocity distribution for both core-collapse and electron-capture supernovae. Comparing the simulated and measured velocities, orbital periods, and eccentricities, we show that the natal kick distribution that can best match the observations is characterized by a bimodal Maxwellian distribution with $\sigma_1$ = 320 km s$^{-1}$ (for core-collapse supernovae) and $\sigma_2$ = 80 km s$^{-1}$ (for electron-capture supernovae) and the He core mass for the latter in the range of $(1.83-2.25)$ $M_{\odot}$. Our findings provide useful insights for further population synthesis and binary evolution studies of NS binaries.