Neurophysiological Markers of Cancer-Related Fatigue Derived from High-Density EEG
Neurophysiological Markers of Cancer-Related Fatigue Derived from High-Density EEG
Handiru, V. S.; Suviseshamuthu, E.; Su, H.; Yue, G. H.
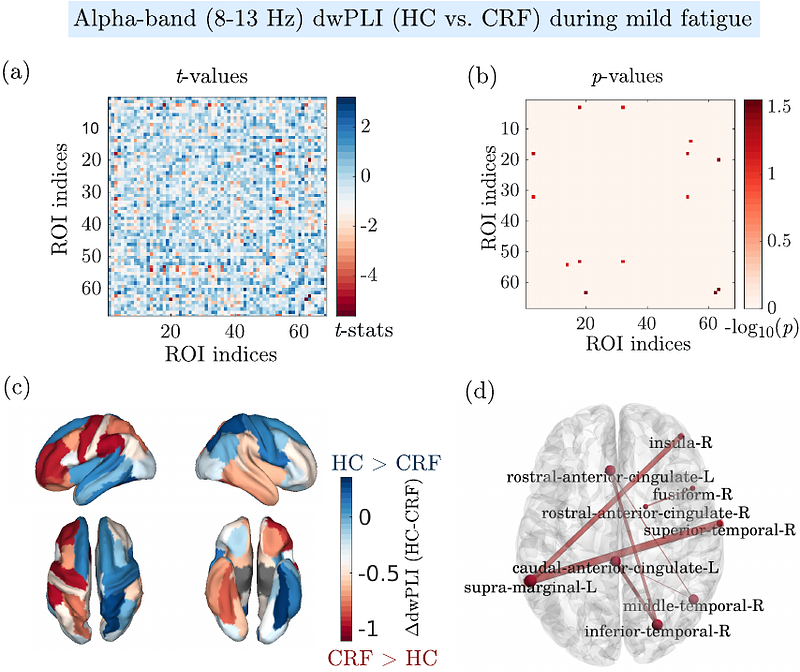
AbstractCancer-related fatigue (CRF) significantly diminishes the quality of life of cancer survivors; however, objective diagnostic markers and the underlying neurophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to identify noninvasive EEG-based biomarkers of CRF by examining cortical activity and functional connectivity. We recorded resting-state and task-related [repetitive submaximal elbow flexion (EFs) until self-perceived exhaustion] high-density electroencephalography (EEG) from 10 cancer survivors with CRF and 14 healthy controls (HC). In our analysis, task-induced fatigue was categorized as mild, moderate, and severe, corresponding to the level of fatigue perceived at the beginning, middle, and end of the task period. Our study revealed the following significant findings: (1) Linear mixed-effects modeling of event-related desynchronization (ERD) EEG analysis during the EF task demonstrated significant effects of group and fatigue levels in the alpha band (8-12 Hz). (2) EF task-specific functional connectivity was estimated using the debiased weighted phase-lag index (dwPLI), which demonstrated reduced inter-regional connectivity in the M1 and prefrontal regions in the CRF group compared with the HC group. (3) The dwPLI analysis identified significantly reduced alpha-band connectivity strength in the CRF group, particularly between the right supramarginal gyrus and other brain regions during mild fatigue. (4) Additionally, resting-state EEG exhibited globally elevated delta band (1-4 Hz) activity in CRF survivors than HC, potentially reflecting chronic fatigue. These observations emphasize the clinical relevance of resting-state EEG, motor activity-related ERD and functional brain connectivity as potential CRF biomarkers. Future research should validate these findings in larger cohorts and provide insights into more objective CRF diagnosis and the development of personalized interventions for alleviating CRF.