Inhibition of ice recrystallization with designed twistless helical repeat proteins
Inhibition of ice recrystallization with designed twistless helical repeat proteins
de Haas, R. J.; Pyles, H.; Huddy, T. F.; van Ossenbruggen, J.; Zheng, C.; van den Broek, D.; Carr, A.; Bera, A.; Kang, A.; Brackenbrough, E.; Joyce, E.; Sankaran, B.; Baker, D.; Voets, I.; de Vries, R.
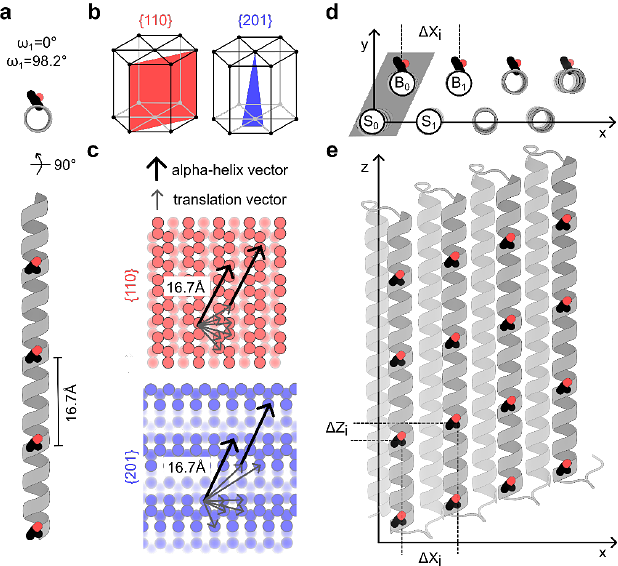
AbstractGiven the repetitive structure of crystalline ice, it is unsurprising that highly active ice-binding proteins, often with beta-roll structures, also have repeating motifs. Here, we introduce a de novo designed family of ice-binding twistless alpha-helical repeat (iTHR) proteins. Each iTHR protein comprises two planar layers of parallel alpha-helices connected by loops-a structural topology not seen in native ice-binding proteins. The ice-binding helices feature an ordered array of TXXXAXXXAXX motifs, spaced to match the pyramidal {201} and secondary prism plane {110} ice lattice facets, and engineered with a 98.2 degree turn angle per residue to orient threonines uniformly towards the ice surface. iTHR proteins show high solubility, thermostability, and produce varied ice crystal morphologies depending on their intended target facet. Crucially, iTHRs exhibit ice recrystallization inhibition (IRI) at critical concentrations comparable to those of many native globular ice-binding proteins. Extensive site-specific mutagenesis shows that ice-binding activity in iTHR proteins is robust, remaining largely unaffected by changes in chemical composition. Variation in the repeat number reveals a non-monotonic relationship to IRI activity. X-ray crystal structures of two designs confirm the intended orientation of threonines, uniformly pointing toward the ice surface. The iTHR family provides a versatile platform to systematically investigate the complex structure-activity relationships underlying protein-ice interactions.