Robotic performance is comparable to human operators for cell therapy manufacturing tasks
Robotic performance is comparable to human operators for cell therapy manufacturing tasks
Sadhu, S.; Schmittlein, B.; Lares, A.; Nayak, S.; Uboldi, M.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Bhanap, P. P.; Ji, Y.; Scheffler, A.; Wilson, J.; Welch, D.; Gkitsas-Long, N.; Retherford, A. J.; Melocchi, A.; Parietti, F.; Feldman, S. A.; Esensten, J. H.
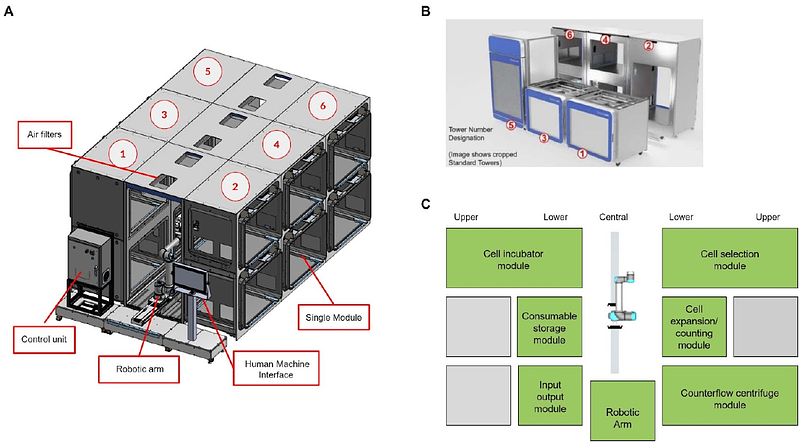
AbstractAutomation in cell therapy manufacturing has the potential to reduce labor costs, decrease variability, reduce contamination risks, and eliminate human errors while enabling rapid manufacturing scale-out. Here we show how a robotic system can precisely and robustly perform a wide variety of tasks (unit operations) common in cell therapy manufacturing. Each of these tasks can be combined by the robot in any order and any number to perform a specific manufacturing process. The robot uses existing modular equipment from market-leading vendors. In each case, we compare the performance of the robot to human operators and establish the accuracy and robustness of the robotic operations. We demonstrate comparability between human and robot for the following operations: bag-to-bag cell transfer, automated cell counting, drawing volume from a vial to a syringe, and cell resuspension and sampling from both a bag and G-Rex 100M-CS bioreactor. Complex processes are also automated, including cell selection using a CytoSinct 1000 and wash/buffer exchange using a CTS Rotea Counterflow centrifugation system. Sterility was maintained during an aseptic process simulation incorporating several of the above unit operations for a generic CAR-T manufacturing process. These data demonstrate that a robotic system can efficiently perform specific unit operations required for the manufacture of a CAR-T drug product and, if linked, the above unit operations can be readily combined to rapidly automate processes that are currently entirely manual.