By: Vadim Kravtsov, Anastasiia Bocharova, Alexandra Veledina, Juri Poutanen, Andrew K. Hughes, Michal Dovčiak, Elise Egron, Fabio Muleri, Jakub Podgorny, Jiři Svoboda, Sofia V. Forsblom, Andrei V. Berdyugin, Dmitry Blinov, Joe S. Bright, Francesco Carotenuto, David A. Green, Adam Ingram, Ioannis Liodakis, Nikos Mandarakas, Anagha P. Nitindala, Lauren Rhodes, Sergei A. Trushkin, Sergey S. Tsygankov, Maimouna Brigitte, Alessandro Di Marco, Noemi Iacolina, Henric Krawczynski, Fabio La Monaca, Vladislav Loktev, Guglielmo Mastroserio, Pierre-Olivier Petrucci, Maura Pilia, Francesco Tombesi, Andrzej A. Zdziarski
We present the results of a three-year X-ray, optical, and radio polarimetric monitoring campaign of the prototypical black hole X-ray binary Cyg X-1, conducted from 2022 to 2024. The X-ray polarization of Cyg X-1 was measured 13 times with the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), covering both hard and soft spectral states. The X-ray polarization degree (PD) in the hard state was found to be $\approx4.0\%$, roughly twice as high as i...
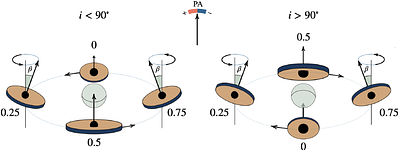
more We present the results of a three-year X-ray, optical, and radio polarimetric monitoring campaign of the prototypical black hole X-ray binary Cyg X-1, conducted from 2022 to 2024. The X-ray polarization of Cyg X-1 was measured 13 times with the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), covering both hard and soft spectral states. The X-ray polarization degree (PD) in the hard state was found to be $\approx4.0\%$, roughly twice as high as in the soft state, where it was around $2.2\%$. In both states, a statistically significant increase of PD with the energy was found. Moreover, a linear relation between PD and spectral hardness suggests a gradual and continuous evolution of the polarization properties, rather than an abrupt change of polarization production mechanism between states. The polarization angle (PA) was independent of the spectral state and showed no trend with the photon energy. The X-ray PA is well aligned with the orientation of the radio jet, as well as the optical and radio PAs. We find significant orbital changes of PA in the hard state, which we attribute to scattering of X-ray emission at intrabinary structure. No significant superorbital variability in PD or PA was found at the period $P_{\rm{so}}$ = 294 d. We also find no correlation between the X-ray and optical polarization; if any, there is a long-term anti-correlation between the X-ray PD and the radio PD.
less