On the computational feasibility of Bayesian end-to-end analysis of LiteBIRD simulations within Cosmoglobe
On the computational feasibility of Bayesian end-to-end analysis of LiteBIRD simulations within Cosmoglobe
R. Aurvik, M. Galloway, E. Gjerløw, U. Fuskeland, A. Basyrov, M. Bortolami, M. Brilenkov, P. Campeti, H. K. Eriksen, L. T. Hergt, D. Herman, M. Monelli, L. Pagano, G. Puglisi, N. Raffuzzi, N. -O. Stutzer, R. M. Sullivan, H. Thommesen, D. J. Watts, I. K. Wehus, D. Adak, E. Allys, A. Anand, J. Aumont, C. Baccigalupi, M. Ballardini, A. J. Banday, R. B. Barreiro, N. Bartolo, S. Basak, M. Bersanelli, A. Besnard, T. Brinckmann, E. Calabrese, E. Carinos, F. J. Casas, K. Cheung, M. Citran, L. Clermont, F. Columbro, G. Coppi, A. Coppolecchia, P. Dal Bo, P. de Bernardis, E. de la Hoz, M. De Lucia, S. Della Torre, P. Diego-Palazuelos, T. Essinger-Hileman, C. Franceschet, G. Galloni, M. Gerbino, M. Gervasi, R. T. Génova-Santos, T. Ghigna, S. Giardiello, C. Gimeno-Amo, A. Gruppuso, M. Hazumi, S. Henrot-Versillé, K. Kohri, L. Lamagna, T. Lari, M. Lattanzi, C. Leloup, F. Levrier, A. I. Lonappan, M. López-Caniego, G. Luzzi, J. Macias-Perez, B. Maffei, E. Martínez-González, S. Masi, S. Matarrese, T. Matsumura, S. Micheli, L. Montier, G. Morgante, L. Mousset, R. Nagata, A. Novelli, I. Obata, A. Occhiuzzi, A. Paiella, D. Paoletti, G. Pascual-Cisneros, F. Piacentini, M. Pinchera, G. Polenta, L. Porcelli, M. Remazeilles, A. Ritacco, A. Rizzieri, M. Ruiz-Granda, J. Sanghavi, V. Sauvage, M. Shiraishi, S. L. Stever, Y. Takase, K. Tassis, L. Terenzi, M. Tomasi, M. Tristram, L. Vacher, B. van Tent, P. Vielva, G. Weymann-Despres, E. J. Wollack, M. Zannoni, Y. Zhou
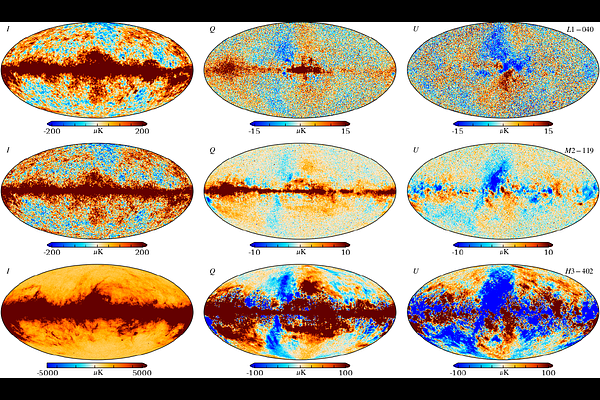
AbstractWe assess the computational feasibility of end-to-end Bayesian analysis of the JAXA-led LiteBIRD experiment by analysing simulated time ordered data (TOD) for a subset of detectors through the Cosmoglobe and Commander3 framework. The data volume for the simulated TOD is 1.55 TB, or 470 GB after Huffman compression. From this we estimate a total data volume of 238 TB for the full three year mission, or 70 TB after Huffman compression. We further estimate the running time for one Gibbs sample, from TOD to cosmological parameters, to be approximately 3000 CPU hours. The current simulations are based on an ideal instrument model, only including correlated 1/f noise. Future work will consider realistic systematics with full end-to-end error propagation. We conclude that these requirements are well within capabilities of future high-performance computing systems.