Origin of the Multi-Phase Interstellar Medium: the Effects of Turbulence and Magnetic Field
Origin of the Multi-Phase Interstellar Medium: the Effects of Turbulence and Magnetic Field
Yue Hu
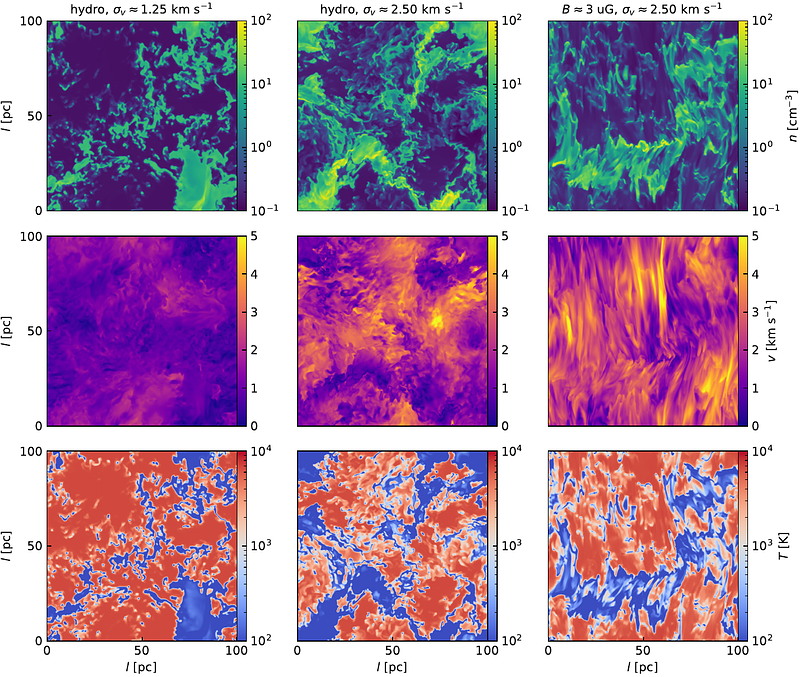
AbstractThe interstellar medium (ISM) consists of a multiphase gas, including the warm neutral medium (WNM), the unstable neutral medium (UNM), and the cold neutral medium (CNM). While significant attention has been devoted to understanding the WNM and CNM, the formation of a substantial fraction of the UNM, with temperatures ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand Kelvin, remains less well understood. In this study, we present three-dimensional hydrodynamical and magnetohydrodynamical simulations of turbulent multiphase ISM to investigate the roles of turbulence and magnetic fields in regulating the multiphase ISM. Our results confirm that turbulence is crucial in redistributing energy and producing the UNM. The turbulent mixing effect smooths the phase diagram, flattens the pressure-density relationship, and increases the fraction of gas in the UNM. We find that magnetic fields not only contribute to sustaining the UNM but also influence the dynamics and distribution of gas across all phases. Magnetic fields introduce anisotropy to the turbulent cascade, reducing the efficiency of turbulent mixing in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. We find the anisotropy results in a less flat phase diagram compared to hydrodynamical cases. Furthermore, the inclusion of magnetic fields shallowens the second-order velocity structure functions across multiple ISM phases, suggesting that more small-scale fluctuations are driven. These fluctuations contribute to the formation of the UNM by altering the energy cascade and thermodynamic properties of the gas. Our findings suggest that the combined effects of turbulence and magnetic fields are important in regulating the multiphase ISM.