The competing effects of recent and long-term star formation histories on oxygen, nitrogen, and stellar metallicities
The competing effects of recent and long-term star formation histories on oxygen, nitrogen, and stellar metallicities
Nicholas Fraser Boardman, Vivienne Wild, Natalia Vale Asari, Francesco D'Eugenio
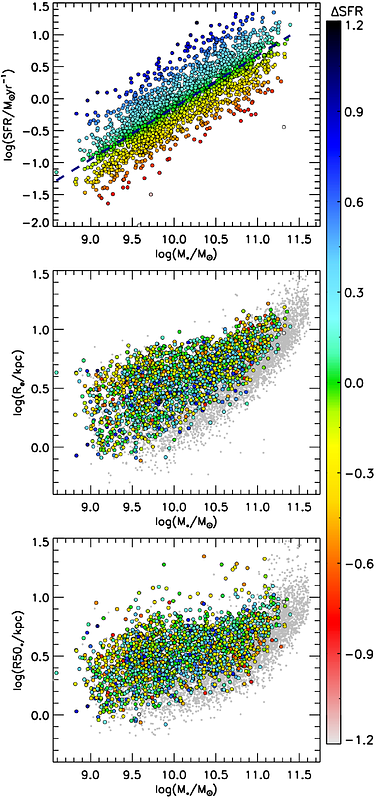
AbstractThe fundamental metallicity relation (FMR) - the three-way trend between galaxy stellar masses, star-formation rates (SFRs) and gaseous metallicities - remains amongst the most studied extragalactic relations. Furthermore, metallicity correlates particularly tightly with gravitational potential. Simulations support a shared origin for these relations relating to long-term gas inflow history variations; however, differences between simulated and observed galaxy samples make it unclear whether this holds for real galaxies. We use MaNGA integral field observations to probe these relations in star-forming galaxies at one effective radius. We confirm the FMR and equivalent relations for stellar metallicity (FMR*) and gaseous N/O (fundamental nitrogen relation, FNR). We find that all relations persist when considering gravitational potential in place of stellar mass and/or considering stellar ages in place of SFR, with the gaseous relations strengthened significantly by considering potential. The gaseous FMR disappears at high masses/potentials, while the FNR persists and the FMR* strengthens. Our results suggest a unified interpretation of galaxies' gaseous and stellar metallicities and their N/O abundances in terms of their formation histories. Deeper gravitational potentials correspond to earlier star-formation histories (SFHs) and faster gas consumption, producing tight potential-abundance relations for stars and gas. In weak potentials, galaxy SFR variations primarily result from recent gas inflows, mostly affecting gas abundances. In deeper potentials, SFR variations instead correspond to broad differences in SFH shapes resulting from differences in long-term gas consumption histories, which is most visible in stellar abundances. This unified interpretation could be confirmed with upcoming higher redshift spectroscopic surveys.