The observable impact of runaway OB stars on protoplanetary discs
The observable impact of runaway OB stars on protoplanetary discs
Gavin A. L. Coleman, Jinyoung Serena Kim, Thomas J. Haworth, Peter A. Hartman, Taylor C. Kalish
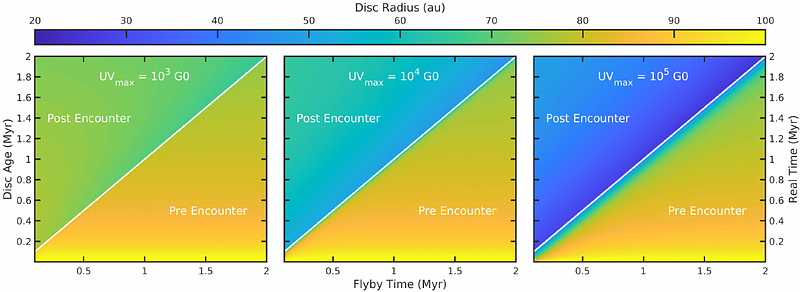
AbstractUV radiation from OB stars can drive ``external'' photoevaporative winds from discs in clusters, that have been shown to be important for disc evolution and planet formation. However, cluster dynamics can complicate the interpretation of this process. A significant fraction of OB stars are runaways, propagating at high velocity which might dominate over the wider cluster dynamics in setting the time variation of the UV field in part of the cluster. We explore the impact of a runaway OB star on discs and the observational impact that may have. We find that discs exposed to even short periods of strong irradiation are significantly truncated, and only rebound slightly following the ``flyby'' of the UV source. This is predicted to leave an observable imprint on a disc population, with those downstream of the OB star vector being more massive and extended than those upstream. Because external photoevaporation acts quickly, this imprint is less susceptible to being washed out by cluster dynamics for faster runaway OB stars. The Gaia proper motion vector of the B star 42 Ori in NGC 1977 is transverse to the low mass stellar population and so may make a good region to search for this signature in resolved disc observations.