Discovery of Main-sequence Radio Pulse emitters from widefield sky surveys
Discovery of Main-sequence Radio Pulse emitters from widefield sky surveys
Barnali Das, Matt E. Shultz, Joshua Pritchard, Kovi Rose, Laura N. Driessen, Yuanming Wang, Andrew Zic, Tara Murphy, Gregory Sivakoff
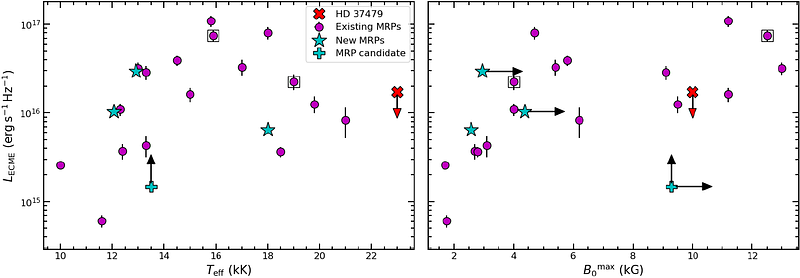
AbstractMagnetic AB stars are known to produce periodic radio pulses by the electron cyclotron maser emission (ECME) mechanism. Only 19 such stars, known as 'Main-sequence Radio Pulse emitters' (MRPs) are currently known. The majority of MRPs have been discovered through targeted observation campaigns that involve carefully selecting a sample of stars that are likely to produce ECME, and which can be detected by a given telescope within reasonable amount of time. These selection criteria inadvertently introduce bias in the resulting sample of MRPs, which affects subsequent investigation of the relation between ECME properties and stellar magnetospheric parameters. The alternative is to use all-sky surveys. Until now, MRP candidates obtained from surveys were identified based on their high circular polarisation ($\gtrsim 30\%$). In this paper, we introduce a complementary strategy, which does not require polarisation information. Using multi-epoch data from the Australian SKA Pathfinder (ASKAP) telescope, we identify four MRP candidates based on the variability in the total intensity light curves. Follow-up observations with the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) confirm three of them to be MRPs, thereby demonstrating the effectiveness of our strategy. With the expanded sample, we find that ECME is affected by temperature and the magnetic field strength, consistent with past results. There is, however, a degeneracy regarding how the two parameters govern the ECME luminosity for magnetic A and late-B stars (effective temperature $\lesssim 16$ kK). The current sample is also inadequate to investigate the role of stellar rotation, which has been shown to play a key role in driving incoherent radio emission.