Conditions for accretion favoring an unmelted Callisto and a differentiated Ganymede
Conditions for accretion favoring an unmelted Callisto and a differentiated Ganymede
Yannis Bennacer, Olivier Mousis, Marc Monnereau, Vincent Hue, Antoine Schneeberger
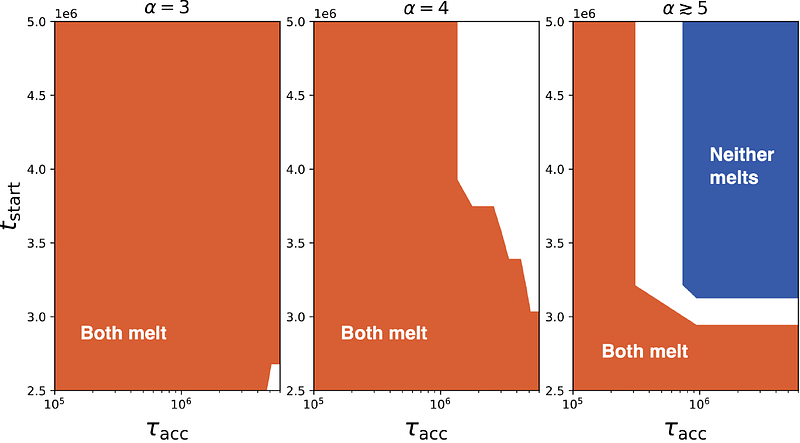
AbstractAnalysis of Callisto's moments of inertia, derived from Galileo's gravity data, suggests that its structure is not fully differentiated. This possibly undifferentiated state contrasts sharply with the globally molten state inferred in its counterpart, Ganymede, and poses unique challenges to theories of the formation and evolution of the Galilean moons. During their formation, both moons experienced multiple heating mechanisms, including tidal heating, radiogenic heating from short-lived radionuclides, accretional heating from impacts, and heat from the surrounding circumplanetary disk. Our study investigates the optimal conditions required to account for Callisto's partially differentiated state in contrast to Ganymede's complete differentiation. We investigate crucial accretion parameters, such as the timing of accretion onset, the duration of accretion, and the impactor size distribution. We find that the observed dichotomy between Ganymede and Callisto can be attributed to similar formation conditions, assuming an identical impactor size distribution and composition in the Jovian circumplanetary disk. The key differences in the formation of Ganymede and Callisto are the disk temperature at their respective formation locations and their final radii. Our results indicate that both moons accreted gradually over more than 2 Myr, concluding at least 5.5 Myr after the formation of calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions in the protosolar nebula. Our model demonstrates that Callisto can remain undifferentiated despite accreting a substantial influx of kilometer-sized impactors, potentially contributing up to 30% of the total mass inflow, while still allowing for the complete differentiation of Ganymede.